REPORTED SPEECH! Direct and Indirect Speech: Verb Tense Changes - https://7esl.com/direct-indirect-speech-tense-changes/ Reported speech is often also called indirect speech in English.
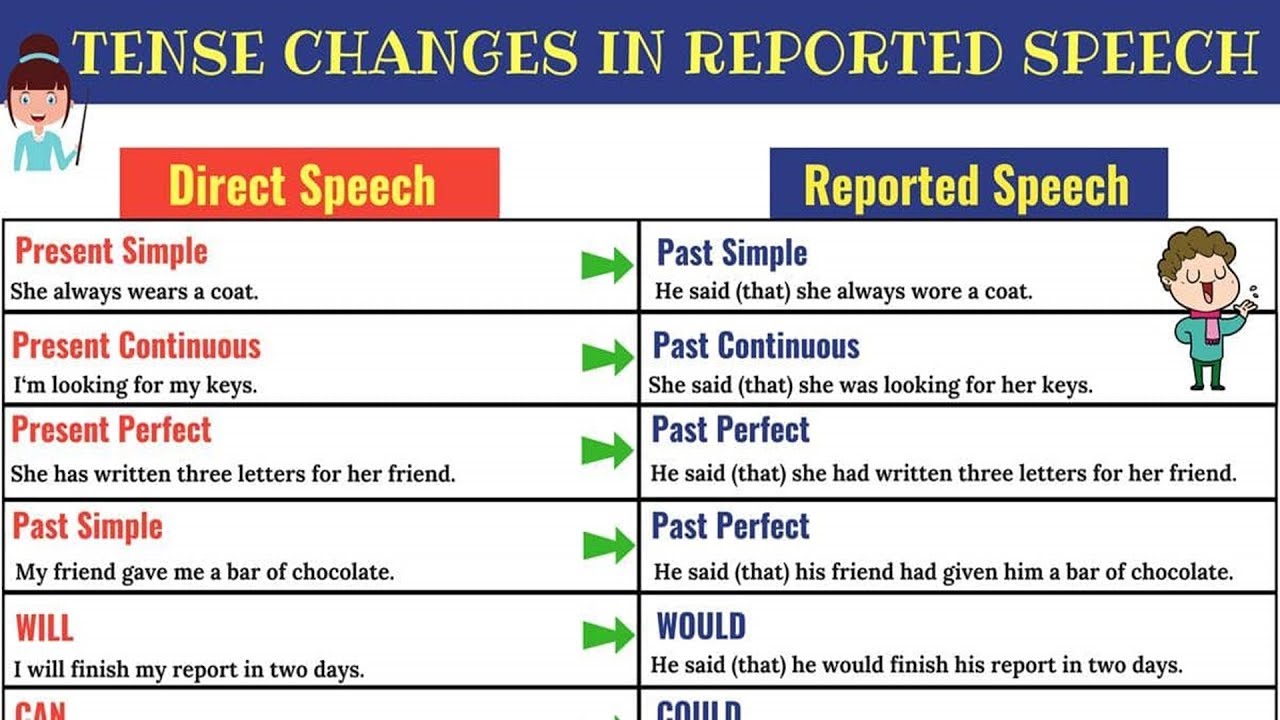
Tense Changes in Reported Speech
Learn how to use Direct and Indirect Speech and Tense Changes When Using Reported Speech.
When changing from direct to indirect speech, you need to change the grammar in certain ways.
Verb tense forms usually need to change. The tenses generally move backwards in this way:
Present Simple Tense into Past Simple Tense
Present Continuous Tense into Past Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Tense into Past Perfect Tense
Past Simple Tense into Past Perfect Tense
Past Continuous Tense into Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Past Perfect Tense (The tense remains unchanged)
Will into Would
Will be into Would be
Will have into Would have
Will have been into Would have been
Other Verb Form Changes in Indirect Speech
Can into Could
Could (The verb remains unchanged)
Have to into Had to
Must into Must/Had to
May into Might
Might (The verb remains unchanged)
Should (The verb remains unchanged)
No Change in Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
There is no change in verb tenses in Indirect Speech when:
The introductory verb is in the Present, Present Perfect or Future.
If the reported sentence deals with a fact or general truth.
The reported sentence contains a time clause.
The verb of the sentence is in the unreal past (the second or the third conditional).
The subjunctive stays unchanged in the subordinate clause.
Had better, could, would, used to, should, might, ought to and mustn’t remain unchanged.
If the speaker reports something immediately or soon after it was said.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WATCH MORE:
★ Grammar: https://goo.gl/pK8eBC
★ Vocabulary: https://goo.gl/d4dJfR
★ Expressions: https://goo.gl/mNKvAB
★ Phrasal Verbs: https://goo.gl/Riw1r6
★ Idioms: https://goo.gl/KrEMRx
★ Conversations: https://goo.gl/MxQEnV
★ Kids Vocabulary: https://goo.gl/K96toU
★ English Writing: https://goo.gl/3zxuQB
★ IELTS: https://goo.gl/5fi2Sk
★ TOEFL: https://goo.gl/3rdyML
★ British vs. American English: https://goo.gl/ySYPWp
★ Pronunciation: https://goo.gl/UXYD2M
★ Business English: https://goo.gl/xpVNkr
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
OUR SOCIAL MEDIA:
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/7english/
Facebook: https://www.fb.com/7ESLLearningEnglish/
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/c/7ESL1
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
For more videos and lessons visit:
https://7esl.com/
Tense Changes in Reported Speech
Learn how to use Direct and Indirect Speech and Tense Changes When Using Reported Speech.
When changing from direct to indirect speech, you need to change the grammar in certain ways.
Verb tense forms usually need to change. The tenses generally move backwards in this way:
Present Simple Tense into Past Simple Tense
Present Continuous Tense into Past Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Tense into Past Perfect Tense
Past Simple Tense into Past Perfect Tense
Past Continuous Tense into Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Past Perfect Tense (The tense remains unchanged)
Will into Would
Will be into Would be
Will have into Would have
Will have been into Would have been
Other Verb Form Changes in Indirect Speech
Can into Could
Could (The verb remains unchanged)
Have to into Had to
Must into Must/Had to
May into Might
Might (The verb remains unchanged)
Should (The verb remains unchanged)
No Change in Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
There is no change in verb tenses in Indirect Speech when:
The introductory verb is in the Present, Present Perfect or Future.
If the reported sentence deals with a fact or general truth.
The reported sentence contains a time clause.
The verb of the sentence is in the unreal past (the second or the third conditional).
The subjunctive stays unchanged in the subordinate clause.
Had better, could, would, used to, should, might, ought to and mustn’t remain unchanged.
If the speaker reports something immediately or soon after it was said.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WATCH MORE:
★ Grammar: https://goo.gl/pK8eBC
★ Vocabulary: https://goo.gl/d4dJfR
★ Expressions: https://goo.gl/mNKvAB
★ Phrasal Verbs: https://goo.gl/Riw1r6
★ Idioms: https://goo.gl/KrEMRx
★ Conversations: https://goo.gl/MxQEnV
★ Kids Vocabulary: https://goo.gl/K96toU
★ English Writing: https://goo.gl/3zxuQB
★ IELTS: https://goo.gl/5fi2Sk
★ TOEFL: https://goo.gl/3rdyML
★ British vs. American English: https://goo.gl/ySYPWp
★ Pronunciation: https://goo.gl/UXYD2M
★ Business English: https://goo.gl/xpVNkr
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
OUR SOCIAL MEDIA:
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/7english/
Facebook: https://www.fb.com/7ESLLearningEnglish/
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/c/7ESL1
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
For more videos and lessons visit:
https://7esl.com/
- Category
- Education
Be the first to comment